Tricks of The Game Programming Gurus - Chapter 2
Hey there, long time since I last posted something up here. I hope you have all been well and are enjoying a good 2025 so far!
This week I picked up on reading a book I started reading last summer, but haven’t had the time to continue at until now. This book’s title is Tricks of The Game Programming Gurus, by André LaMothe, one of my favourites. It’s about video game design and development from the DOOM and Wolfenstein era. Here’s a picture of the book’s cover:
When I last got into reading this book, I was able to get some of the examples of Chapter 2 working in a modern environment, and now that I’m picking it up again I realise that I never shared my progress in my very blog!. Here is a repost of a comment I made on a GitHub repository dedicated to this book. Enjoy!
…
For future readers,
After some trial and error, I managed to set up a working development environment for chapter 2! In the end, I opted for using DOSBox, plus a couple of enviornments to make it all build and link together.
Here’s a step by step guide I crafted along the way:
DOSBox
Simply download DOSBox for your OS. I’ve left a link to their downloads page down in the references.
Once installed, mount your C drive as some local directory in your host machine. I just made a directory called DOSPROGS/ in my Desktop and that worked just fine.
Assembler (MASM611)
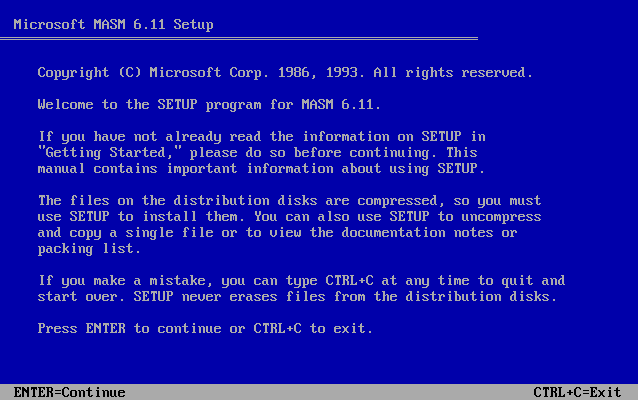
Get Microsoft Macro Assembler, link in the references! Then, extract the disks’ content to a folder in your MS DOS C Drive. I settled for C:\DOSPROGS\MASM611\.
From DOS’ command line, run the SETUP.EXE file that comes with MASM611. The installer will then prompt you with an installation screen. Follow the instructions and select all the defaults you see fit.
C
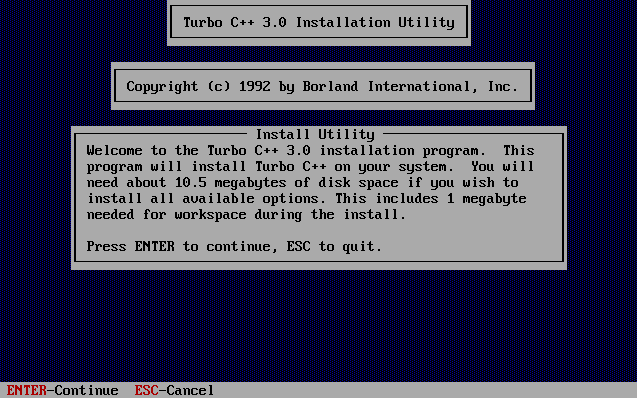
Get Borland Turbo C++, link in the references! Much like you did with MASM, extract the disks’ content to a folder in your MS DOS C Drive. I used C:\DOSPROGS\TCC\.
From DOS’ command line, run the INSTALL.EXE file that comes with TCC. The installer will then prompt you with an installation screen. Follow the instructions and it will install accordingly. Also, at one point in the installation process, TCC will ask you what folder it should install itself to. In my case, I selected C:\TC\.
Assembling, Compiling, Linking and Running
Step 1: Assembling
First off, you will have to write down an assembly file and use MASM to assemble it. Here’s a listing taken from the book:
Listing 2.8 - An assembly procedure to set the video mode (SETMODEA.ASM)
.MODEL MEDIUM, C
.CODE
PUBLIC Set_Mode
Set_Mode PROC FAR C vmode:WORD
mov AH,0
mov AL, BYTE PTR vmode
int 10h
ret
Set_Mode ENDP
END
To assemble with MASM:
CD C:\MASM611\BIN
MASM SETMODEA.ASM;
This will create a SETMODEA.OBJ file. Keep this file around, you will have to link it later!
Step 2: Compiling
Now, you will need the C function that calls what you have defined in your ASM file. Save the following listing to a file:
Listing 2.9 - A C function to test the video mode (SETMODEC.C)
#include <stdio.h>
#define VGA256 0x13
#define TEXT_MODE 0x03
extern Set_Mode(int mode);
void main(void)
{
// This sets the video mode to 320x200, 256 colour mode.
Set_Mode(VGA256);
// Wait for keyboard to be hit.
while (!kbhit()) {}
// Put the computer back into text mode.
Set_Mode(TEXT_MODE);
} // end main
To compile with TCC:
CD C:\TC\BIN
TCC -IC:\TC\INCLUDE -mm -c SETMODEC.C;
This will create a SETMODEC.OBJ file. Keep this file around, you will have to link it later!
Step 3: Linking
Still from the TC directory, bring SETMODEA.OBJ into it, and link it together with SETMODEC.OBJ. You may do so as follows:
TLINK c0m SETMODEC.OBJ SETMODEA.OBJ,SETMODE.EXE,,cm -LcC:\TC\LIB
Step 4: Run!
Simply run the executable file to test the results:
SETMODE.EXE
Notes
The -mm flag passed to TCC, and the arguments c0m and cm passed to TLINK represent the type of memory model that’s being used for the program. In this case, it’s all ms because we’re using the MEDIUM model.
Like so, you must replace these arguments to work with other models accordingly:
- TINY:
-mt;c0tandct. - SMALL:
-ms;c0sandcs. - COMPACT:
-mc;c0candcc. - MEDIUM:
-mm;c0mandcm. - LARGE:
-ml;c0landcl. - HUGE:
-mh;c0handch.
Well, that’s it! I’ll keep on reading now, hopefully this guide will help you get started.
References & Downloads
- DOSBox - https://www.dosbox.com/download.php?main=1
- Microsoft Macro Assembler 6.11 (3.5) (MASM611) - https://winworldpc.com/product/macro-assembler/6x
- Borland Turbo C++ 3.0 (3.5-720k) (TC) - https://winworldpc.com/product/turbo-c/3x